The Merge: Ethereum Transition From PoW to PoS

Table of Contents:
In a key update known as “The Merge,” Ethereum shifted from employing energy-intensive technology to a more sustainable approach a few minutes before 3 a.m. Eastern time on Sept. 15.
The price of Ether, or ETH — the platform’s native cryptocurrency — remained largely stable in the hours following the merge. It was just 5% lower nine hours after the merge compared to the price at the time of the transfer.
Essentially, this long-awaited merge upgrade is Ethereum’s transition from its current “Proof-of-Work (PoW)” system to a “Proof-of-Stake (PoS)” system. This technological revamp of the world’s second-most valuable cryptocurrency by market capitalization took years to complete.
The beacon chain, which debuted in December 2020, and the Ethereum chain, which launched in July 2015, were both successful. The technology behind the merge was tested for over two years on the Beacon chain, which ran alongside Ethereum’s initial Mainnet network.
When the merge happened, the information on Mainnet was moved to the Beacon chain – a mid-flight rocket-engine switch in Ethereum terminology.
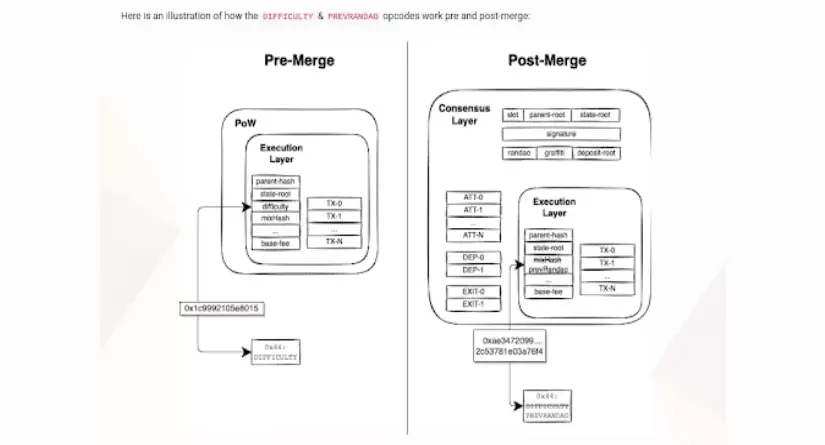
The consensus procedures in each chain were distinct. Only PoS will remain after the merge; PoW will cease to exist. According to EIP-3675.
Aside from that, EIP-4399 is also in use. This alters the semantics of the return result of the current DIFFICULTY (0x44) opcode and renames it PREVRANDAO (0x44).
The Merge: An Overview

Since Ethereum’s launch in 2015, the Mainnet blockchain has employed a technique known as proof-of-work to securely add new transactions and other information.
Proof-of-work compels user computers to solve increasingly harder computations before they can contribute a new block – and reap cryptocurrency rewards.
This strategy is called mining and is used by many cryptocurrencies, including Bitcoin. Although mining is secure, it uses a lot of energy. On an annual basis, the Ethereum network utilizes the same amount of energy that some whole nations do in the same time frame.
Proof-of-stake is a less energy-intensive solution. Instead of sacrificing electricity, which supplies processing power, users who wish to participate in the verification process stake their personal bitcoin in a process known as staking.
These people, known as validators, are chosen at random to validate new information uploaded to a block. They will be paid in bitcoin, provided they deliver accurate information. They risk losing their share if they act dishonestly.
Post-Merge Status Quo: Heads Up For The Investors
It’s hard to predict how the merge will play out in the long run, but investors should keep the following points in mind:
No Work Required
According to the network’s website, if you held ETH before the merge, you don’t need to do anything.
Beware of the Scammers
Ethereum urges users to be wary of scammers who claim that they need to upgrade or transfer to a new token, such as “ETH2.” There is no such token.
Token Congestion
Because mining payments, which are bigger than staking rewards, are no longer paid out, the rate at which new ETH tokens enter circulation has decreased by around 90%.
No Change In Cost
Congestion and high transaction costs, particularly gas fees, have long been a source of contention for Ethereum. The merge had no immediate effect on any of these problems.
Transfer of Power
The network will be propelled forward by the wealth of “stakers” rather than the computing power.
Increase In Traffic
Upcoming updates might expand the number of participants in the Ethereum network by allowing devices such as phones to become nodes, perhaps alleviating the congestion stated above.
Categories
Have A Question?
BrainX Technologies
UNITED STATES
600 N Broad Street, Suite 5 # 409
Middletown, DE 19709
+13156365350 (Sales)
PAKISTAN
27, L-Block, Johar Town
Lahore, Pakistan
+924238913038 (Careers) | +923334686651 (Sales)
Copyright © 2022 BrainX Technologies. All rights reserved.
